Key Concepts¶
In this document, we introduce some important concepts in GraphScope analytical engine, which defines the graph loading strategies, inner/outer vertices, and message passing and synchronization strategies.
LoadStrategy¶
There are three ways to maintain the nodes crossing different fragments in GraphScope analytical engine.
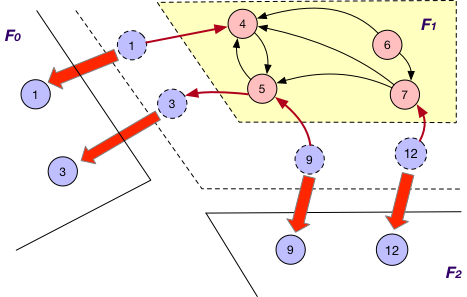
OnlyOut¶
Each fragment
OnlyIn¶
Under this case, each fragment
BothInOut¶
Each fragment
PartitionStrategy¶
Edge Cut¶
An edge cut partitioning splits vertices of a graph into roughly equal size clusters. The edges are stored in the same cluster as one or both of its endpoints. Edges with endpoints distributed across different clusters are crossing edges.
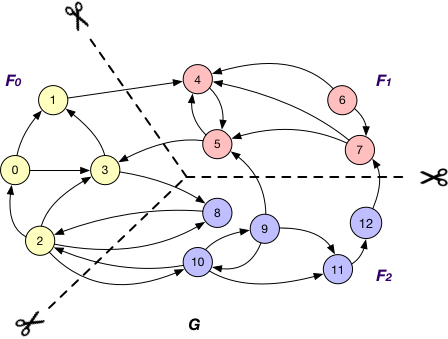
Vertex Cut¶
A vertex-cut partitioning divides edges of a graph into roughly equal size fragments. The vertices that hold the endpoints of an edge are also placed in the same fragment as the edge itself. A vertex has to be replicated when its adjacent edges are distributed across different fragments.
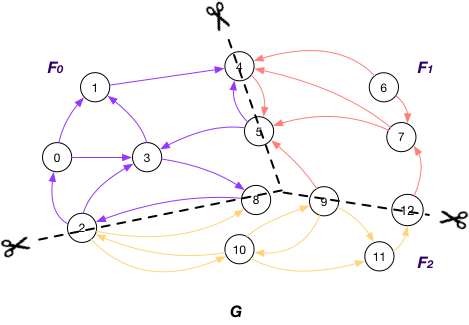
Vertices on GraphScope analytical engine¶
A node v is referred to as an
OuterVertex¶
OuterVertex of fragment
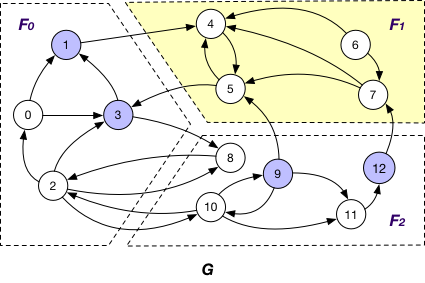
InnerVertex¶
InnerVertex of fragment
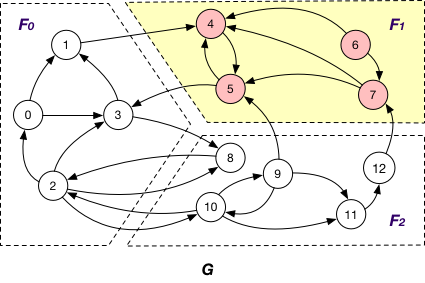
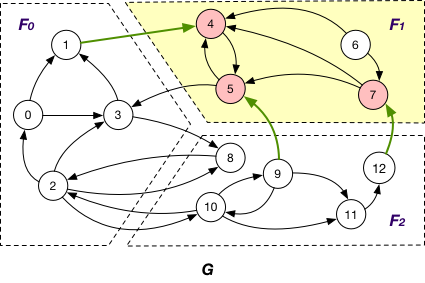
InnerVertexWithOutgoingEdge¶
InnerVertexWithOutgoingEdge of fragment
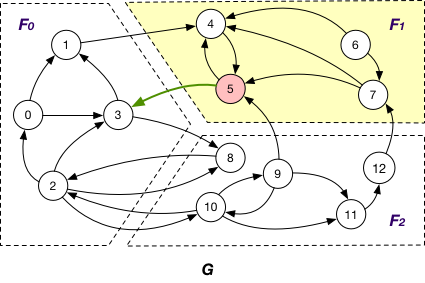
InnerVertexWithIncomingEdge¶
InnerVertexWithIncomingEdge of fragment
MessageManager and MessageStrategy¶
In each graph application in GAE, a MessageManager is created to manage the messages passed between different fragments. Considering the diversity of graph applications, we provide many message passing strategies, which are defined in MessageStrategy.
Below are message passing and synchronization strategies supported by GAE.
AlongOutgoingEdgeToOuterVertex¶
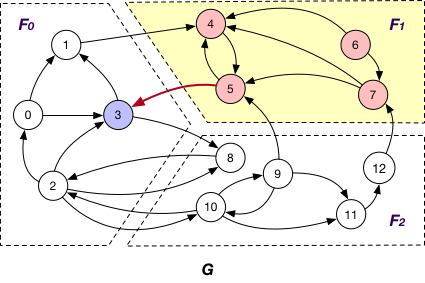
Here the message is passed along crossing edges from InnerVertexWithOutgoingEdge to OuterVertex. For instance, the message is passed from node 5 to 3 in graph G.
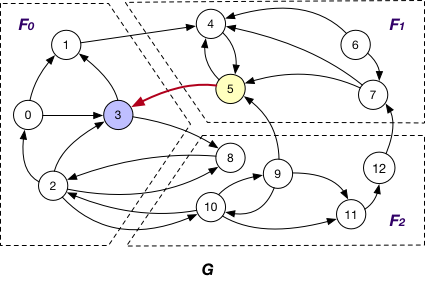
AlongIncomingEdgeToOuterVertex¶
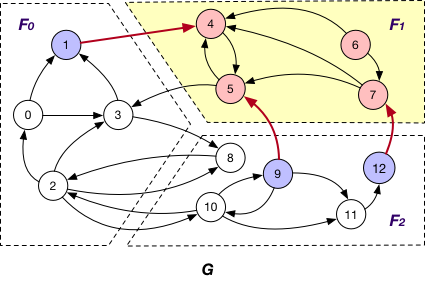
Under this case, the message is passed along crossing edges from InnerVertexWithIncomingEdge to OuterVertex. For example, the message is passed from node 5 to 9 in graph G.
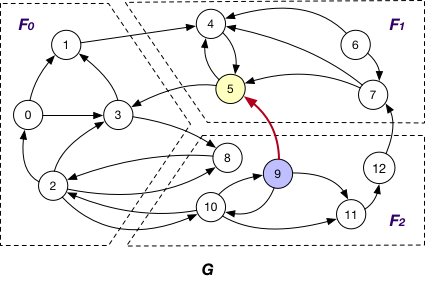
AlongEdgeToOuterVertex¶
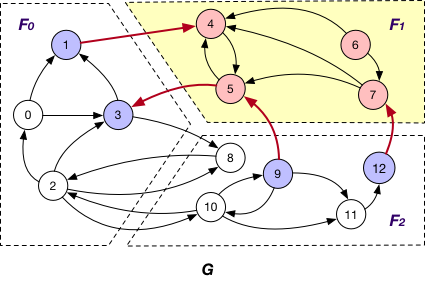
Each message is passed along crossing edges from nodes that are both InnerVertexWithIncomingEdge and InnerVertexWithOutgoingEdge to OuterVertex, e.g., messages are passed from node 5 to 3 and 9 and vice versa in graph G.
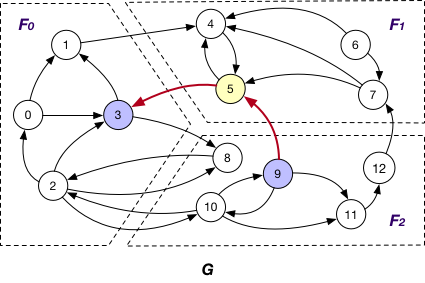
SyncOnOuterVertexAsTarget¶
It is applied in company with the OnlyOut loading strategy. Here each fragment
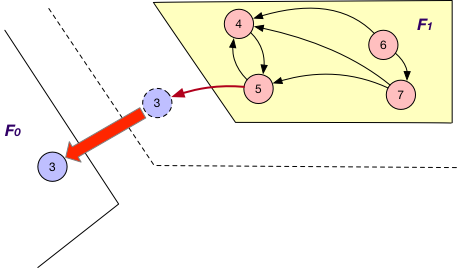
SyncOnOuterVertexAsSource¶
It is applied together with the OnlyIn loading strategy. Similar to SyncStateOnOuterVertexAsTarget, each fragment
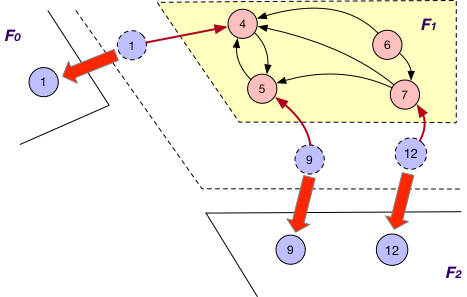
SyncOnOuterVertex¶
This is applied together with the BothInOut loading strategy. Under this case, each fragment